You can download the full April–June 2019 QSM results (2.4MB, PDF) or view the commentary and interactive charts below.
Local DHB report
Falls
Process marker 1: Percentage of older people assessed for the risk of falling
Nationally, 87 percent of older patients* were assessed for their falls risk in quarter 2, 2019 (Figure 1). This marker has dropped below the expected achievement level of 90 percent for the last two quarters. Prior to this, the target was achieved most quarters since quarter 4, 2013.
At the district health board (DHB) level, nine out of 20 DHBs achieved the expected marker level for this current quarter and three of them have remained at this level for at least six continuous quarters. Bay of Plenty, Hutt Valley, Northland and Taranaki DHBs have consistently not met the expected marker level since quarter 4, 2012. Nelson Marlborough DHB has moved to the lower group in the assessment for the risk of falling from quarter 4, 2017 due to data collection changes.
Falls T 1
- Upper group: ≥ 90 percent
- Middle group: 75–89 percent
- Lower group: < 75 percent
* Patients aged 75+ (55+ for Māori and Pacific peoples)
Process marker 2: Percentage of older people assessed as at risk of falling who received an individualised care plan that addresses these risks
About 93 percent of patients assessed as being at risk of falling had an individualised care plan completed (Figure 2). This measure has increased 16 percentage points compared with the baseline in quarter 1, 2013. Achievements vary across DHBs. In quarter 2, 2019, there were 16 DHBs in the upper group compared to 14 in quarter 1, 2019. Nelson Marlborough, South Canterbury and Southern DHBs have been consistently lower than the national average in the development of an individualised care plan. Northland has remained in the upper group since quarter 4, 2018. Canterbury, Counties Manukau, Hutt Valley, Waitematā and Whanganui DHBs have been consistently present in the upper group for more than six consecutive quarters.
Falls T 2
- Upper group: ≥ 90 percent
- Middle group: 75–89 percent
- Lower group: < 75 percent
When assessments and care plans are plotted against each other, a trend of movement over time is shown from the bottom left corner (low assessment and individualised care plan) to the top right corner (high assessment and individualised care plan) in Figure 3. Five DHBs sat at the top right corner in quarter 1, 2013; in quarter 2, 2019, nine DHBs are in this ‘ideal’ box (see Figure 3), down from ten DHBs the last quarter. Ten DHBs met the care plan rate target but did not meet the assessment rate baseline.
Falls T 3
Outcome marker: In-hospital falls resulting in a fractured neck of femur per 100,000 admissions
There were 92 falls resulting in a fractured neck of femur (broken hip) in the 12 months ending June 2019.
To control the impact of changes in the number of admissions and to capture special causes of variation with a more robust time-series, the results will be reported quarterly instead of monthly. Figure 4 shows the quarterly rate of in-hospital falls causing a fractured neck of femur per 100,000 admissions.
The median of this measure was 12.8 in the baseline period of July 2010 to June 2012. It had moved down since September 2014, to 9.4 per 100,000 admissions, and shown a significant improvement. This reduction is supported by the observed improvement in the assessment and plan process markers results. There are some variations, especially in quarter 2, and quarter 3, 2018. Further analysis needs to understand the causes of these variations.
Falls T 4
The number of 92 in-hospital falls resulting in a fractured neck of femur is significantly lower than the 115 we would have expected this year, given the falls rate observed in the period between July 2010 and June 2012. The in-hospital falls reduction is estimated to have saved $1.06 million from July 2018 up until June 2019. This is based on an estimate of $47,000[1] for a fall with a fractured neck of femur (Figure 5).
We know some of these patients are likely to be admitted to aged residential care on discharge from hospital, which is estimated to cost $135,000 per occurrence.[2]
If we conservatively estimate that 20 percent of the patients who avoided a fall-related fractured neck of femur would have been admitted to an aged residential care facility, the reduction in falls represents $1.46 million in total avoidable costs since July 2018.
Falls T 5
Hand hygiene
National compliance with the five moments for hand hygiene remains high.
Process marker 1: Percentage of opportunities for hand hygiene taken
National compliance with the five moments for hand hygiene remains high. Nationally, DHBs maintained an average of 85 percent compliance for the period April–June 2019 compared with 62 percent in the baseline in July–October 2012. Hauora Tairāwhiti and Taranaki DHBs have been consistently below the national target of 80 percent.
HH T 1
- Upper group: ≥ 70 percent before quarter 3, 2014, 75 percent in quarters 3 and 4, 2014, and 80 percent since quarter 1, 2015.
- Middle group: 60 percent to target.
- Lower group: < 60 percent.
- Hand hygiene national compliance data is reported three times every year, not quarterly.
Outcome marker: Healthcare associated Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia (SAB) per 1,000 bed-days
Healthcare associated SAB can be associated with medical devices or surgical procedures which means the onset of symptoms may occur outside of the hospital (community onset).
Figure 7 displays the monthly healthcare associated SAB per 1,000 bed-days. Data for the last month, June, is omitted, due to denominator completeness issues. From May 2017, the median has significantly increased from 0.11 to 0.13 per 1,000 bed-days. We are working with DHBs to better understand this shift and will monitor closely in the coming quarters.
HH T 2
Surgical site infection improvement (SSII) – orthopaedic surgery
As the Commission uses a 90-day outcome measure for surgical site infection (SSI), the data runs one quarter behind other measures. Information in this section relates to hip and knee arthroplasty procedures from quarter 3, 2013 to quarter 1, 2019.
Process marker 1: Antibiotic administered in the right time
For primary procedures, an antibiotic should be administered in the hour before the first incision (‘knife to skin’). As this should happen in all primary cases, the threshold is set at 100 percent. In quarter 1, 2019, 98 percent of hip and knee arthroplasty procedures involved the giving of an antibiotic within 60 minutes before knife to skin. Six DHBs achieved the national goal. Counties Manukau, Northland and Waitematā DHBs have consistently been below the upper group since quarter 3, 2013.
SSII OS T 1
- Upper group: 100 percent
- Middle group: 95–99 percent
- Lower group: < 95 percent
Process marker 2: Right antibiotic in the right dose – cefazolin 2 g or more or cefuroxime 1.5 g or more
In the current quarter, 97 percent of hip and knee arthroplasty procedures received the recommended antibiotic and dose. Seventeen of the 20 DHBs reached the threshold level of 95 percent compared with only three in the baseline quarter.[3] In quarter 1, 2019, West Coast DHB has moved to the lower group.
SSII OS T 2
- Upper group: ≥ 95 percent
- Middle group: 90–94 percent
- Lower group: < 90 percent
Outcome marker: SSIs per 100 hip and knee operations
In quarter 1, 2019 (January up until March) there were 38 SSIs out of 2,442 hip and knee arthroplasty procedures, a quarterly SSI rate of 1.56 percent, which is higher than the current median of 0.9 percent since August 2015. There were four consecutive points above the median since December 2018 and a peak rate of 2.32 percent in January 2019. It could be an early indication of a significant upwards shift, but we will monitor closely in the coming quarters. Information on the month of April is not reported.
SSII OS T 3
Surgical site infection improvement (SSII) – cardiac surgery
This is the tenth quality and safety marker (QSM) report for cardiac surgery. Since quarter 3, 2016 all five DHBs performing cardiac surgery have submitted process and outcome marker data from all cardiac surgery procedures, including coronary artery bypass graft with both chest and donor site, and with chest site only. There are three process markers and one outcome marker, which are similar to the markers for orthopaedic surgery.
Process marker 1: Timing – an antibiotic to be given 0–60 minutes before knife to skin
The target is for 100 percent of procedures to achieve this marker. Auckland DHB paediatric achieved the target this quarter and Southern DHB has continued to meet the target for three successive quarters.
SSII CS T 1
- Upper group: 100 percent
- Middle group: 95–99 percent
- Lower group: < 95 percent
Process marker 2: Dosing – correct antimicrobial prophylaxis used in at least 95 percent of procedures
The antibiotic prophylaxis of choice is ≥ 2 g or more of cefazolin for adults and ≥ 30 mg/kg of cefazolin for paediatric patients, not to exceed the adult dose. The target is that either dose is used in at least 95 percent of procedures. All DHBs performing cardiac surgery except Canterbury achieved the target this quarter.
SSII CS T 2
- Upper group: > 95 percent
- Middle group: 90-95 percent
- Lower group: < 90 percent
Process marker 3: Skin preparation – appropriate skin antisepsis is always used
Appropriate skin antisepsis in surgery involves alcohol/chlorhexidine or alcohol/povidone iodine. The target is 100 percent of procedures achieving this marker. All DHBs except Southern achieved the target this quarter.
SSII CS T 3
- Upper group: 100 percent
- Middle group: 95–99 percent
- Lower group: < 95 percent
Outcome marker: SSIs per 100 procedures rate
In March 2018 we see the median shift downwards from 4.8 SSI cases per 100 cardiac procedures to 4.0. This is a significant improvement since the beginning of the SSII Programme. Cardiac surgical services in DHBs are dedicated to ensuring high compliance with the process measures in addition to implementing other quality improvement activities such as an anti-staphylococcal bundle.
SSII CS T 4
Safe surgery
This is the twelfth report for the safe surgery QSM, which measures levels of teamwork and communication around the paperless surgical safety checklist.
Direct observational audit was used to assess the use of the three surgical checklist parts: sign in, time out and sign out. A minimum of 50 observational audits per quarter per part is required before the observation is included in uptake and engagement assessments. Rates are greyed out in the tables below where there were fewer than 50 audits.
Figure 15 shows how many audits were undertaken for each part of the checklist. Fifteen out of the 20 DHBs achieved 50 audits for all three parts in quarter 2, 2019. Counties Manukau Health has a large auditor cohort, which explains its high numbers.
SS T 1
Rates for uptake (all components of the checklist were reviewed by the surgical team) are only presented where at least 50 audits were undertaken for a checklist part. Uptake rates were calculated by measuring the number of audits of a part where all components of the checklist were reviewed against the total number of audits undertaken.
The components for each part of the checklist are shown in the poster on the right. Of the 15 DHBs that achieved 50 audits in each checklist, 11 achieved the 100 percent uptake target in at least one part of the checklist, during the current quarter (see Figure 16). Data is not presented where there were fewer than 50 audits.
SS T 2
The levels of team engagement with each part of the checklist were scored using a seven-point Likert scale developed by the World Health Organization. A score of 1 represents poor engagement from the team and 7 means team engagement was excellent. The target is that 95 percent of surgical procedures score engagement levels of 5 or above. As Figure 17 shows, for the latest quarter Bay of Plenty, Hawke’s Bay, MidCentral, Northland, Southern, Wairarapa and Whanganui DHBs achieved the target in all three parts. Eight other DHBs achieved the target in one or two parts – a decrease from twelve DHBs last quarter. Data are not presented where there were fewer than 50 audits.
SS T 3
The safe surgery quality and safety domain now includes a start-of-list briefing measure to reinforce the importance of the briefing as a safe surgery intervention. The measure is described as ‘Was a briefing including all three clinical teams done at the start of the list?’
Figure 18 shows, in quarter 2, 2019, 12 DHBs reported that a start-of-list briefing was happening. There is no specific target for this part of the measure; the aim is to have all 20 DHBs increasingly undertaking and reporting briefings over time. The programme team continues to work with the auditing teams to increase data submission rates so the report better matches practice in DHBs.
SS T 4
The rates of postoperative sepsis and deep vein thrombosis/pulmonary embolism (DVT/PE) are the two outcome markers for safe surgery. The rates have fluctuated over time. To understand the factors driving the changes and to provide risk-adjusted outcomes in the monitoring and improvement of surgical QSMs, we have developed a risk-adjustment model for these two outcome markers.
The model identifies how likely patients being operated on were to develop sepsis or DVT/PE based on factors such as their condition, health history and the operation being undertaken. From this, we calculated how many patients would be predicted to develop sepsis or DVT/PE based on historic trends. We then compare how many patients actually developed sepsis or DVT/PE to create an observed/expected (O/E) ratio. If the O/E ratio is more than 1 then there are more sepsis or DVT/PE cases than expected, even when patient risk is taken into account. A ratio of less than 1 indicates fewer sepsis or DVT/PE cases than expected.
Figure 19 shows the DVT/PE risk-adjustment model results in two charts. The O/E ratio control chart shows there were 11 consecutive quarters in which the observed numbers were below the expected numbers since quarter 2, 2013. This indicates a statistically significant downwards shift, taking into account the increasing number of high-risk patients treated by hospitals and more complex procedures undertaken by hospitals. Over the past three years, a higher number of cases of DVT/PE have been observed in the second quarter. In the most recent six quarters, the O/E ratio is higher than the median value of 0.93. We will closely monitor this in future quarters to see if there is enough evidence of a shift up.
SS T 5
Medication safety – electronic medicine reconciliation
This quality and safety domain focuses on medicine reconciliation where the process is supported with electronic data capture. Medicine reconciliation is a process by which health professionals accurately document all medicines a patient is taking and their adverse reactions history (including allergy). The information is then used during the patient’s transitions in care. An accurate medicines list can be reviewed to check the medicines are appropriate and safe. Medicines that should be continued, stopped or temporarily stopped can be documented on the list. Reconciliation reduces the risk of medicines being:
- omitted
- prescribed at the wrong dose
- prescribed to a patient who is allergic
- prescribed when they have the potential to interact with other prescribed medicines.
The introduction of electronic medicine reconciliation (eMedRec) allows reconciliation to be done more routinely, including at discharge. There is a national programme to roll out eMedRec throughout the country. Figures 20 and 21 show there are six DHBs that have implemented the system to date. Further uptake of eMedRec is limited until the IT infrastructure is improved in each DHB hospital.
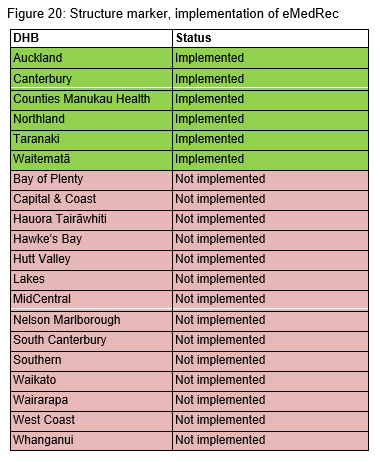
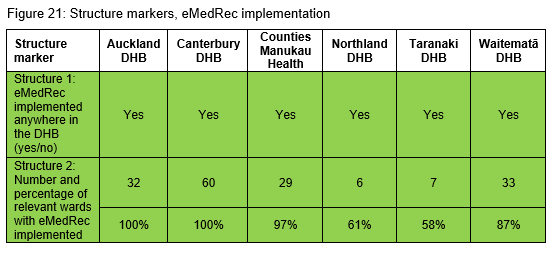
Within the six DHBs that have implemented eMedRec, only Northland and Taranaki DHB hospitals are reporting their process markers. Figure 22 shows the process marker change over time for these two DHBs. Further work is being undertaken on refining and agreeing the eMedRec marker definitions. Once this has been achieved the other DHB hospitals using eMedRec will report their process markers.
MS T 1
Patient deterioration
This is the fifth quarter that structural, process and outcome measures for the patient deterioration QSMs have been reported.
DHBs were asked to provide both process and outcome measure data by ethnicity where possible. Despite an increase in ethnicity data submitted from the previous quarter, we have not included this in the national report because the majority of DHBs were still unable to submit. We acknowledge that, for some DHBs, it will take more time to start collecting and submitting ethnicity-level data.
Structural measure: Eligible wards using the New Zealand early warning score
The structural measure demonstrates the progress DHBs have made towards implementing improvements to their recognition and response systems and aligning with the New Zealand early warning score (NZEWS).
The majority of DHBs (90 percent, n=18) have now implemented or are in the process of implementing the NZEWS in their hospitals. We have also seen an increase in the use of the tool across all eligible wards from the last quarter (now at 98 percent). Note: the structure measure of national level is calculated based only on those DHBs that have implemented the NZEWS.
PD T 1
Process measure 1: Correct calculation of early warning score
The first process measure (Figure 24) shows the percentage of audited patients with an early warning score calculated correctly for the most recent set of vital signs. This measure demonstrates how the recognition part of the system is working through the correct use of the NZEWS. We’ve introduced a threshold to indicate relative groupings for this quarter. Results for this measure show a national figure of 94 percent for this quarter.
Eighteen DHBs (90 percent) submitted data for this measure. Those using an electronic vital signs system in all their eligible wards will be able to achieve 100 percent consistently for this measure. While Southern DHB is yet to implement the NZEWS, they have reported data using their existing EWS.
PD T 2
Process measure 2: Appropriate response to escalations
The second process measure (Figure 25) shows the percentage of audited patients that triggered an escalation of care and received the appropriate response to that escalation as per the DHB’s agreed escalation pathway. This measure demonstrates how the response part of the system is working through the appropriate response to care that has been escalated.
The national figure for this measure was 75 percent, an increase from the previous quarter of 64 percent. There was considerably more variation between DHBs than for the first process measure, highlighting an opportunity for improvement. The Commission is currently working with DHBs to understand this variation in particular regarding the consistency of data collected, the sample size and timeframes regarding the escalation pathway. A total of 17 DHBs (85 percent) submitted data for this measure.
PD T 3
Outcome measure 1: Rate of in-hospital cardiopulmonary arrests (preliminary results)
The following outcome measures will be used over time to determine whether the improvements to hospitals’ recognition and response systems have improved patient outcomes. Both measures are shown in a rate per 1,000 admissions. It is important to note that the preliminary admissions data used to calculate the rate is taken from the National Minimum Dataset (NMDS) at a DHB level and may differ from rates generated from administrative systems locally.
The results (Figure 26) show a national rate of 1.5 cardiopulmonary arrests per 1,000 admissions for this quarter. Fifteen DHBs provided data for this measure. Canterbury DHB is not displayed this quarter because it is currently developing systems to capture cardiac arrest data.
PD T 4
Outcome measure 2: Rate of rapid response escalations (preliminary results)
The second outcome measure (Figure 27) shows the rate of rapid response escalations per 1,000 admissions (excluding those mentioned previously). Consistent with the previous quarter, the results showed a national rate of 32 events per 1,000 admissions. Fifteen DHBs (75 percent) provided data for this measure.
International research has shown that an effective recognition and response system will result in an inverse relationship between outcome measures 1 and 2 (ie, a higher rate of rapid response escalations with a lower rate of in-hospital cardiopulmonary arrests). Another outcome measure used internationally is unplanned admissions to intensive care units. See the patient deterioration domain of the Atlas of Healthcare Variation for these data.
PD T 5
To further investigate the relationship between process measures 1 and 2 we have developed a scatterplot. The aim over time, is to have all DHBs locate in the top right corner which reveals a high rate of NZEWS scoring accuracy and appropriate response. It shows all DHBs that supplied data had a high rate of early warning score calculated correctly but there is more variation across all DHBs in the reported rates of appropriate response.
PD T 6
Pressure injury
We aim to reduce the occurrence of and harm from pressure injuries. Pressure injuries (also known as pressure ulcers, decubitus ulcers, pressure areas and bed sores) are a cause of preventable harm for people using health care services, including hospital, aged residential care and home or community care.
Pressure injuries are often avoidable, have significant negative impact on patient’s lives, whānau, and those providing their care, increase hospital length of stay and are associated with extra resource consumption.
Following implementation of the pressure injury QSM in July 2018 the majority of DHBs (95 percent, n=19) are now submitting data. This is the second quarter that process and outcome measures have been reported publicly. Following a review of data this quarter we are planning to engage with DHBs to better understand local data collection processes.
Process measure 1: percentage of patients with a documented and current pressure injury risk assessment
The first process measure (Figure 29) shows the percentage of patients with a documented and current pressure injury risk assessment. This measure is used to monitor how well DHBs are conducting pressure injury risk assessments and recognising at-risk patients. This includes those at risk of developing a pressure injury and those with an existing pressure injury.
Results for this measure revealed a national figure of 83 percent, an increase from 81 percent during last quarter.
A total of 19 DHBs (95 percent) submitted data for this measure.
PI T 1
Process measure 2: Percentage of at-risk patients with a documented and current individualised care plan
The second process measure (Figure 30) shows the percentage of at-risk patients with a documented and current individualised care plan designed to address any risk (prevention) or manage any existing pressure injuries. This measure is used to monitor how well DHBs are putting in actions to prevent or manage pressure injuries for at-risk patients.
The national figure for this measure was a rate of 84 percent, an increase from 80 percent during last quarter.
A total of 18 DHBs (90 percent) submitted data for this measure.
PI T 2
Outcome measure 1: Percentage of patients with hospital-acquired pressure injury
The following outcome measures will be used over time to determine whether the improvements to prevention and management of pressure injuries have improved patient outcomes.
The first outcome measure (Figure 31) shows the percentage of patients with hospital acquired pressure injuries (ie, pressure injuries that formed while the patient was in hospital).
The national figure for this measure was a rate of 4.1 percent, an increase from 3.5 percent during last quarter. There is also considerable variation between DHBs highlighting an opportunity for improvement. We are working with DHBs to improve consistency of data collection.
A total of 18 DHBs (90 percent) submitted data for this measure.
PI T 3
Outcome measure 2: Percentage of patients with a non-hospital-acquired pressure injury
The second outcome measure (Figure 32) shows the percentage of patients with non-hospital-acquired pressure injuries (ie, patients that arrived at hospital with a pressure injury that was formed in aged residential care, at home or in community care.)
The national figure for this measure was a rate of 1.5 percent, a small increase from 1.4 percent during last quarter. There is also considerable variation for this outcome measure highlighting an opportunity for improvement.
A total of 18 DHBs (90 percent) submitted data for this measure.
PI T 4
References
- de Raad J–P. 2012. Towards a value proposition: scoping the cost of falls. Wellington: NZIER.
- Ibid.
- In quarter 1, 2015, 1.5 g or more of cefuroxime was accepted as an alternative agent to 2 g or more of cefazolin for routine antibiotic prophylaxis for hip and knee replacements. This improved the results of this process measure for MidCentral DHB significantly, from 10 percent before the change to 96 percent immediately after the change. It also increased the national result from 90 percent to 95 percent in quarter 1, 2015.
