Sepsis guides and tools for health professionals
Resources – including guidance and tools – designed to support the early recognition and treatment of sepsis.
Resources – including guidance and tools – designed to support the early recognition and treatment of sepsis.
This clinical guide covers the recognition, diagnosis and early management of sepsis. It is for health care professionals working in primary, secondary and tertiary care. People who have experienced sepsis and their family/whānau can use it as a care standard. This guide:
Raise the Flag: Sepsis quality improvement: Clinical governance for sepsis supports the effective implementation and long-term sustainability of the national sepsis improvement package. It includes a summary of the clinical governance framework to help health care professionals deliver and embed the national sepsis pathway.
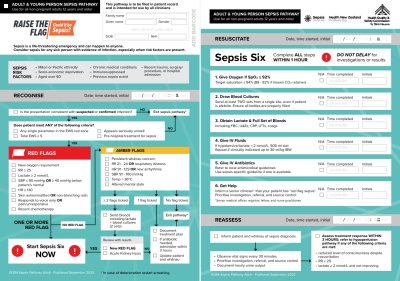
The sepsis pathways are endorsed by Health New Zealand | Te Whatu Ora.
Hospital sepsis guides and pathways
Pre-hospital community sepsis pathways
Use these templates to:
A range of evidence-gathering activities have informed the development of the national sepsis quality improvement package, including national and international literature scoping reviews, analysis of sepsis-related adverse events, and a stocktake of sepsis management across New Zealand.
Together, this work identified harm associated with sepsis, variation in current practice, and clear opportunities for system-level improvement.
Key findings and reports from this scoping phase are outlined below.
Literature scoping review by Callan Attwell
HQSC Sepsis Quality Improvement Scoping Review 2023 (PDF 1 MB)
Sepsis adverse event thematic analysis
Sepsis scoping summary report
Sepsis quality improvement programme scoping summary (PDF 1.2MB)
Stocktake of sepsis management in New Zealand
Stocktake of sepsis management in Aotearoa New Zealand (PDF 1.5 MB)